Graphs: The Connectors of the Data World 🌐 - Part 1
Part 15 of data structures series. Let's discover the theory behind Graphs data structure!
Welcome to Graphville 🏙️. Imagine this: you're navigating a city where every building, street, and landmark is connected in some way. But instead of just walking around, you’re in charge of mapping and managing these connections using the Graph Data Structure. Exciting, right? Grab your map🗺 and compass🧭️, because this guide is going to make exploring graphs a thrilling urban adventure 🏙️🛤️!
In this first part of our series, we'll dive into the basics of what graphs are, how they work, and why they’re super important. The goal is to make you feel like a Graph Wizard 🧙 by the end of it, without overwhelming you, haha. Ready? Let's go!
What Exactly Is a Graph? 🤔
Imagine you’re trying to make new friends in a city. Each person you meet can be represented by a node (or vertex) and each friendship (relationship) is a connection between nodes, called an edge. These relationships could be one-way or mutual. Congratulations, you’ve just visualized a graph!
A Sneaky, Simple Example 🕵️♂️
Let’s break it down with something more relatable: Social Media. Imagine you're creating a new profile on a social networking platform. Here's how it would work:
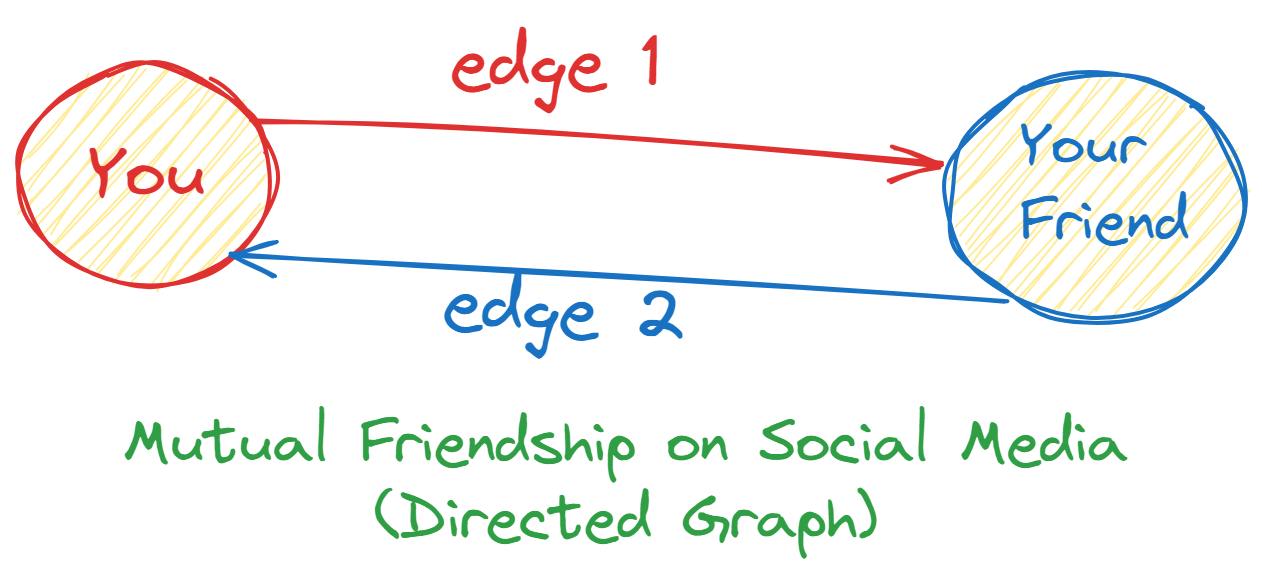
You (let’s call you Node A) have a friend (Node B).
You follow Node B, but they might not follow you back. Or, maybe you’re mutual friends and both of you follow each other.
And voilà! You have a graph! Your relationship with Node B is represented as an edge connecting both nodes.
Key Terms That You’ll Totally Nail After This 💡
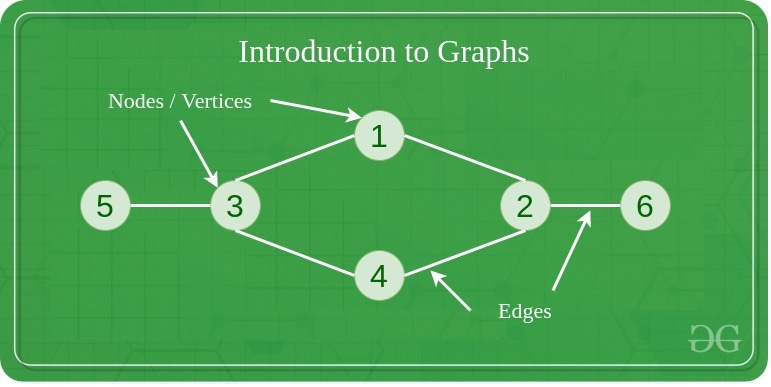
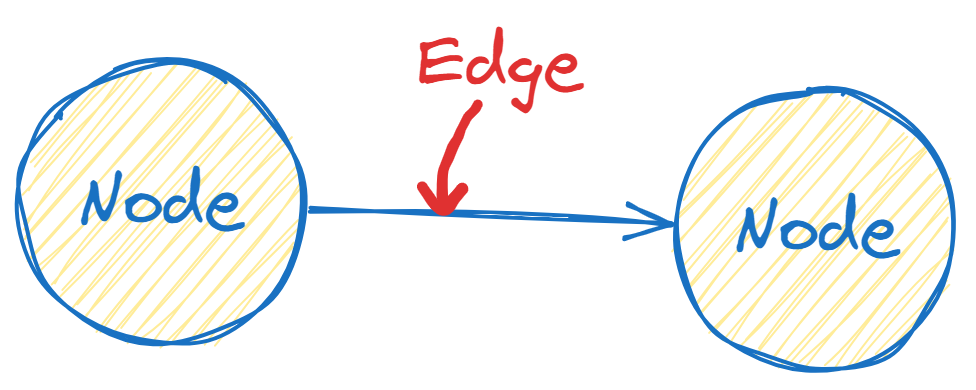
Node (Vertex): A point in the graph where data (or objects) are stored. Think of it as a place, person, or thing.
Example: People on social media, cities on a map, or webpages on the internet
Edge: A line connecting two nodes, representing a relationship.
Example: Friendship, road connections, or hyperlinks between websites
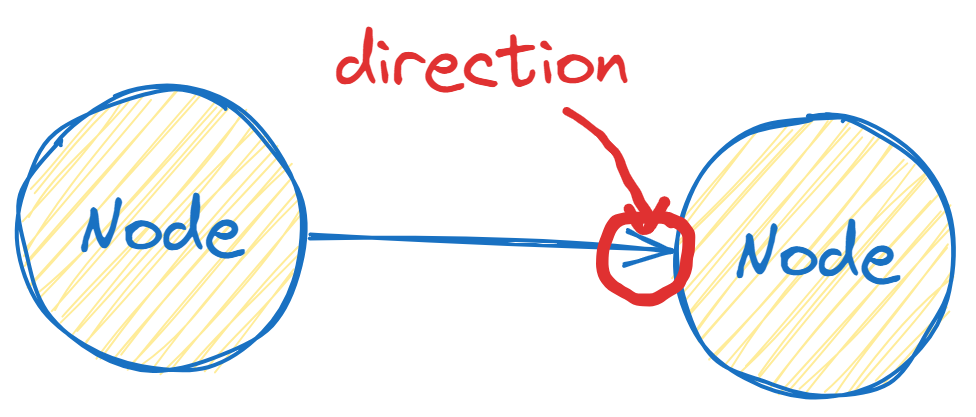
Directed Graph (Digraph): A graph where edges have directions. Imagine a one-way street; you can drive only in one direction.
Example: Twitter follows (you can follow someone without them following you back)
Undirected Graph: A graph where edges have no direction. Think of it as a two-way street; you can drive both ways.
Example: Facebook friendships (both need to agree to become friends).
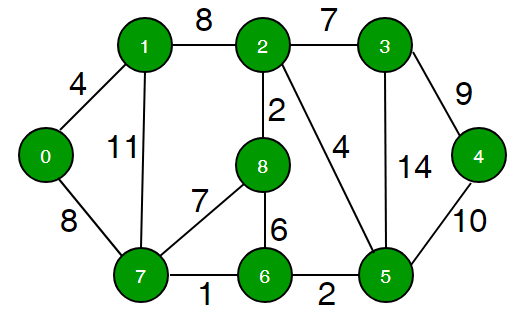
Weighted Graph: Here, each edge carries some weight or cost. This could represent distance, time, or any measure.
Example: Maps! The edge weight can be the distance between two cities.
Unweighted Graph: A graph where all edges are treated equally. The focus is just on connections, not on any specific values.
Types of Graphs 🎨
Let's take a tour of different types of graphs you might encounter in this magical graph world. Each type has its own quirky behavior!
1. Simple Graph 🧾
Contains no loops or multiple edges between the same pair of nodes.
Ideal for: Basic networks where relationships between nodes are simple.
2. Complete Graph 🕸
Every node is connected to every other node. It’s like a social circle where everyone knows everyone else!
Ideal for: Fully connected networks like team collaboration.
3. Directed Graph (Digraph) 🚦
All edges have directions.
Ideal for: Situations like web page ranking (Google’s PageRank), where the importance of one page is determined by the links leading to it.
4. Weighted Graph 🏋️♀️
Edges have weights to represent distance, time, or cost.
Ideal for: Map-based apps like Google Maps, where distance matters.
5. Tree 🌲
A special type of graph with no cycles. It has a root node and branches out.
Ideal for: Hierarchical structures, like organizational charts or file systems.
Fun Challenge: Can You Guess the Graph? 🎮
Let’s play a game! I’ll describe a real-world scenario, and you try to guess which type of graph would represent it:
Scenario 1:
You are a delivery driver using Google Maps to navigate from point A to point B. You need to avoid heavy traffic and find the quickest route. Question: What kind of graph are you dealing with?
💡Hint: You’re working with distances (weights) between locations (nodes)!
Scenario 2:
You and your friends have a group chat where everyone can message everyone else. No one has special privileges, and anyone can talk to anyone. Question: What kind of graph is this? 💡Hint: No one-way messages here, communication is open both ways!
Solution down here 👇:
Weighted Graph: because we’re working with distances (weights) between locations (nodes)!
Complete Graph: because we’re communicating in both ways!
Wrapping Up 🎊: You're Now a Graph Explorer! 🧭
By now, you should have a strong foundational understanding of what graphs are and how they apply to real life. You’ve learned about nodes, edges, and the different types of graphs, from directed to weighted. You’ve even explored how they power our digital world, from social networks to GPS.
And this is just Part 1! In the next part, we’ll dive deeper into algorithms like graph traversal (sounds fancy, right?) and how we can use graphs to solve more complex problems.
Until then, keep exploring, because the world of graphs is vast and connected—literally! 🌐
Stay tuned for Part 2, where we'll get hands-on and dig into graph algorithms. Spoiler alert: We’ll be traversing graphs and solving puzzles! 😎
🔔 Don't forget to subscribe to my blog and YouTube channel to stay updated with all the latest content, follow me on LinkedIn too, if you like to do so!